Raster Graphics & Vector Graphics

I was speaking to a newer graphic designer on LinkedIn, having a conversation about specific uses for different graphics types. After explaining that you can rasterize any vector graphic, it opened the question to them: For media imagery, logos, and kits...why even start with non-vectors?
Well, it's about use cases and media types. Read more and we'll talk a bit about it...
Raster Graphics vs. Vectors: What’s the Difference?
As a graphic designer, you’re likely to encounter two main types of digital images: raster graphics and vector graphics. Understanding the difference between them is essential because it will help you choose the right format for each project. Let’s break down what these two are, and how they differ from each other.
"Vector graphics are digital art that is rendered by a computer using a mathematical formula. Raster images are made up of tiny pixels, making them resolution-dependent and best used for creating photos."
What are Raster Graphics?
Raster graphics are made up of tiny squares called pixels. Each pixel has its own color, and when combined, they form an image. Think of it like a digital photograph or a painting made from little blocks of color.
Key characteristics of raster graphics:
- Pixels: The image is made of millions of small pixels. The more pixels, the clearer and sharper the image looks.
- File Formats: Common raster file formats include JPG, PNG, GIF, TIFF, and BMP.
- Resolution: The quality of a raster image depends on its resolution. Higher resolution means more pixels and better quality, but it also means larger file sizes. Low-resolution images can look blurry or pixelated if they are enlarged too much.
Examples of raster graphics:
- Digital photos
- Scanned artwork
- Complex, detailed images with lots of color gradients
When to use raster graphics:
- Photographs or images with complex color details and textures.
- When you need to display rich, realistic images, like web images or print photos.
What are Vector Graphics?
Vector graphics are created using mathematical formulas that define shapes, lines, and curves. Unlike raster graphics, which rely on pixels, vector images are made up of paths, which can be scaled infinitely without losing quality.
Key characteristics of vector graphics:
- Paths, not pixels: A vector image uses lines, curves, and shapes defined by mathematical equations. These paths are resolution-independent.
- File Formats: Common vector file formats include SVG, AI (Adobe Illustrator), EPS, and PDF.
- Scalability: The biggest advantage of vector graphics is that they can be resized without any loss of quality. You can make a logo tiny or blow it up to billboard size, and it will still look crisp and sharp.
Examples of vector graphics:
- Logos
- Icons
- Illustrations and drawings
- Charts and graphs
When to use vector graphics:
- When you need to create graphics that can be scaled up or down, like logos, icons, or illustrations.
- For designs that will be used in a variety of sizes and formats, such as business cards, posters, and websites.
☄️Raster Vs. Vector: Explaining It Simply!
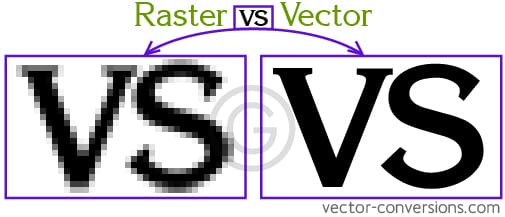
Imagine a picture is made of tiny blocks. Those tiny blocks are called pixels, and together they make up a raster graphic. This is how things like photos or detailed images work. But here’s the thing: if you try to make a raster image bigger, it can get blurry because the blocks are fixed in size. So, you can’t make a photo bigger without losing quality.
Now, think of a vector graphic as a picture made with lines and shapes. These aren’t blocks, but paths drawn with math. The cool thing about vectors is that you can make them as big or as small as you want without losing any quality because the paths adjust to fit the size. So, no blurriness!
Another difference is the file size. A photo (raster image) with lots of details can be very large, especially if it’s high resolution (super sharp). On the other hand, vector images are usually smaller, even if they look complicated, because they only need to store information about the paths, not individual pixels.
When it comes to editing, raster images (like photos) can be harder to tweak if you want to change something later. With vector graphics, it’s much easier to adjust things, like resizing or changing colors, because they’re based on shapes and lines that are easy to modify.
In short:
- Raster = pictures made of pixels (good for photos, but can get blurry if resized)
- Vector = pictures made of lines and shapes (good for logos and illustrations, and you can resize them without any problems)
"Vector graphics are created using paths, which are defined by mathematical equations, allowing for infinite scalability without loss of quality. This makes them ideal for designs like logos, icons, and illustrations. To work with vector graphics, several Free and Open Source Software (FOSS) tools are available, such as Inkscape, a powerful vector graphics editor that's often compared to Adobe Illustrator. Another great tool is Krita, primarily known for digital painting, but it also offers vector support. Additionally, Vectr is an easy-to-use, web-based vector design tool suitable for beginners. These FOSS options provide great alternatives to proprietary software, allowing users to create and manipulate vector artwork efficiently." -Mal
Which Should You Use?
It depends on the type of project you’re working on! Here’s a quick guide to help you decide:
- Use raster graphics for photographs, detailed artwork, and textures.
- Use vector graphics for logos, icons, and illustrations that need to be scaled without losing quality.
At the end of the day:
As a graphic designer, learning the strengths and limitations of both raster and vector graphics will make you more versatile in your design projects. Remember that there’s no one-size-fits-all solution — both have their uses, and knowing when to use each will make you a more effective designer.

Member discussion